Principles of Zoning in Urban Town Planning

Definition
It is the distribution or division of land (in town planning) into particular zones based upon some criteria or principles.
Principles of Zoning
The principles of zoning refer to the fundamental concepts and guidelines that govern the process of dividing land into different zones or districts for specific uses and development. Zoning is an important tool in urban planning and land use management. The principles of zoning include the following elements which are given importance while zoning an area. Here's an explanation of the principles of zoning:
- Concentric growth
- Boundary
- Existing towns
- Flexibility
- New towns
a. Concentric growth
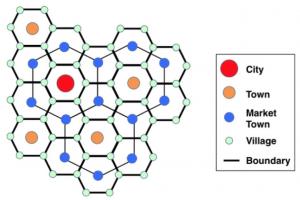
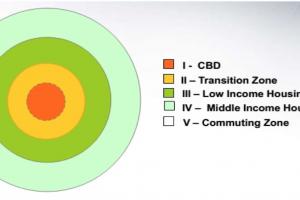
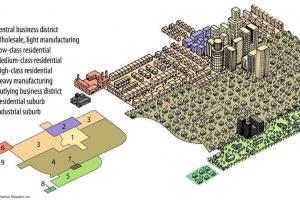
The usual pattern of zones is in the form of concentric bands. The central area of town is followed by developed area, green area & undeveloped area.
The growth of buildings spreads from a center in all directions is called concentric growth. These types of buildings usually form a ring and consist of residential buildings surrounded by commercial areas. This type of growth is natural and totally unplanned. When the population goes on the increase, the concentric circles are again surrounded by people - these areas are called the suburbs of the city.
The principle of concentric growth suggests organizing zones in a concentric pattern around a central core or central business district (CBD). This concept proposes a gradual transition of land use from the CBD outwards, with zones becoming progressively less dense or more suitable for residential uses as the distance from the core increases. This principle aims to achieve efficient land use and transportation systems by locating complementary land use in close proximity.
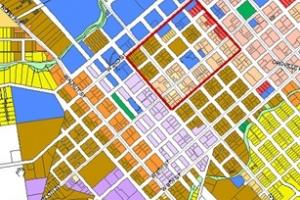
b. Boundary
The design of boundaries for different zones should be carefully made. The boundaries should be a street, road, railway line, park, or open green space. Boundaries are an important element in zoning. Usually, the boundaries between two zones can be a road, railway line, river, wall, or green belt. Green belt is preferred to all others. The existence of boundaries depends on the rule of law. Sometimes boundaries are broken and two zones seem to mix. This type of area is then called a transition zone.
Zoning principles often involve the establishment of clear boundaries between different zones. Boundaries help demarcate areas designated for specific uses, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or recreational purposes. Boundaries also provide clarity to developers, residents, and local authorities regarding permitted uses and development regulations within each zone.
c. Existing towns
While zoning and planning new towns, the planner must keep in mind the convenience of existing towns. Zoning should be done in such a way as not to disturb the ecosystem of the already existing towns. Zoning principles take into account existing towns and urban areas. These principles consider the preservation and enhancement of established communities by allowing for compatible land uses and promoting their continued vitality. Existing towns are typically allocated specific zones to accommodate their unique character, historical significance, and development needs.
d. Flexibility
The principles of zoning may be rigidly enforced. but at the same time, care should be taken to observe flexibility in working out the details for zoning. The zoning of an area should be such so as to provide maximum comfort and convenience to people. Zoning should also be done in such a way that in the future new towns can be made and there is room for expansion of the zone. Zoning principles recognize the need for flexibility and adaptability in land use regulations. They acknowledge that circumstances may change over time, requiring adjustments to zoning regulations to accommodate evolving needs and challenges. Flexibility in zoning allows for modifications in land use designations, zoning standards, or development regulations to respond to changing social, economic, and environmental conditions.
e. New towns
For designing a new town of a known population the areas required for residence, industries, and business are clearly marked. The town is then divided into suitable zones. New towns should be provided room for zoning of sites. For designing a new town with a known population the areas required for residence, industries & businesses are clearly marked. The town is then divided into suitable zones. Zoning principles also consider the development of new towns or planned communities. These principles provide guidelines for designing and implementing comprehensive zoning plans for new areas. Zoning regulations ensure the integration of various land uses, such as residential, commercial, recreational, and green spaces, in a coordinated and sustainable manner.