Advantages and Limitations of Prestressed Concrete
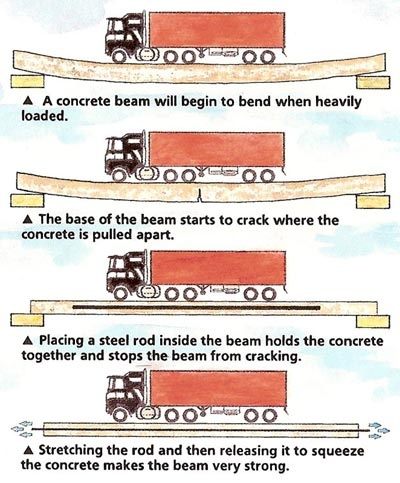
Advantages of Pre-Stressed Concrete:
The pre-stressing of concrete has several advantages as compared to traditional reinforced concrete (RC) without pre-stressing. A fully prestressed concrete member is usually subjected to compression during service life. This rectifies several deficiencies of concrete. The following text broadly mentions the advantages of a pre-stressed concrete member with an equivalent RC member. For each effect, the benefits are listed.
Increased Structural Strength:
Pre-stressed concrete significantly enhances the structural strength and load-carrying capacity of the members. The precompression applied to the concrete reduces or eliminates tensile stresses, minimizing the risk of cracking and increasing the resistance to bending, shear, and deflection.
Greater Span Lengths:
Pre-stressed concrete allows for longer span lengths compared to traditional reinforced concrete. By introducing prestressing forces, it becomes possible to construct bridges, beams, and slabs with larger unsupported spans, reducing the need for intermediate supports and enhancing the aesthetics of the structure.
Reduction in Structural Depth:
The introduction of pre-stressing forces allows for a reduction in the overall depth of structural elements. This benefit is particularly advantageous in buildings or structures with space constraints, as it maximizes usable floor space while maintaining structural integrity.
Crack Control and Durability:
Prestressed concrete minimizes the occurrence and width of cracks, especially in areas subjected to high tensile stresses. By applying compressive stresses, prestressed concrete increases the resistance to shrinkage, temperature changes, and long-term creep, thus enhancing the durability and longevity of the structure.
Efficient Material Usage:
Prestressed concrete optimizes the use of construction materials. The high strength of prestressed concrete allows for the reduction in the cross-sectional area of structural members, resulting in efficient material utilization and potential cost savings.
Resistance to Dynamic Loads:
Pre-stressed concrete exhibits superior resistance to dynamic loads, such as those experienced during earthquakes or heavy vibrations. The pre-compression in the concrete helps to counteract the effects of external forces, improving the structural response and reducing the risk of failure.
Limitations of Pre-stressing
Although prestressing has advantages, some aspects need to be carefully addressed:
Complexity and Specialized Techniques:
The construction of prestressed concrete requires specialized knowledge, equipment, and techniques. It involves pre-tensioning or post-tensioning processes, which can be more complex than traditional reinforcement methods. Skilled labor and careful quality control are necessary to ensure proper execution.
Higher Initial Costs:
Prestressed concrete structures often involve higher initial costs compared to conventionally reinforced concrete. The materials, equipment, and labor required for prestressing can contribute to increased project expenses. However, the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and longer service life may outweigh the initial investment.
Limited Flexibility for Modifications:
Once prestressed concrete members are constructed, modifications or alterations can be challenging and costly. Unlike reinforced concrete, where additional reinforcement can be easily added or modified, pre-stressed concrete requires careful consideration and planning for any changes in the future.
Special Considerations for Corrosion Protection:
If not properly protected, the pre-stressing tendons in prestressed concrete structures can be susceptible to corrosion. Adequate measures must be taken during design and construction to prevent exposure to moisture, chloride ions, or other corrosive elements, which may require additional protective measures and regular maintenance.
Design and Engineering Expertise:
Designing prestressed concrete structures requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Structural engineers must account for the preloading forces, stressing procedures, and potential variations in material properties to ensure safe and efficient designs. Collaboration with experienced professionals is essential to achieve the desired results.