Definitions in Waste Water Treatment
Sludge Volume Index (SVI-TEST)
It is the measure of the settleability and compatibility of sludge and is made from a laboratory column setting test.
Definition
The sludge volume index is defined as ‘the volume in mm occupied by 1 gm of sludge after it has settled for a specified period of time’ generally ranging from 20 min to 1 or 2 hr in a 1 – or 2-l cylinder. One-half hour is most common setting time allowed to the mixed liquor to settle for 30 min. ( larger cylinder is desirable to minimize bridging of sludge floe and war effects). Take the reading let Vs is the settled volume of sludge (ml/l) in 30 min.
* If SVI is 50 - 150 ml/mg, the sludge settle ability is Good.
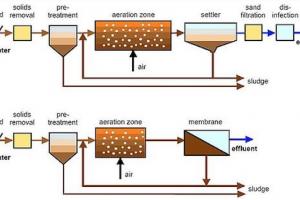
Return Activated Sludge System:
- The activated sludge form the underflow of the final setting tanks should be returned to the inlet of the aeration tanks at a rote sufficient to maintain the MLSS concentration at the design value.
- The flow are needed for return-sludge is determined form the incoming sewage flow rate and the concentration at which the sludge is with drawn form the final setting tanks.
Hence a simple measure of the underflow concentration form the setting tanks is required. The parameter conventionally employed for this purpose the sludge volume index, SVI which is defined as 4 the volume occupied by sludge containing 1.0g of sludge soiled (dry weight) after 30 min setting and thus it has ht units ml/g. Some time represented as SDI i.e sludge density index. Once the SVI and operating MLSS concentration (x) is known, the required rate of activated sludge return can be determined
R = 100 / [ 106/ (x) (SVI) -1] where r = return sludge flow rate as a % age of incoming sewage flow.
SEDIMENTATION:
It is the removal of solid particles form a suspension by settling under gravity.
CLARIFICATION:
It is a similar term which refers specifically to the function of a sedimentation removal.
THICKENING:
It means the separation of water from Suspended Solids where R = return sludge flow rate (ML/D) for Q in ML/D)
SURFACE GEOMETRY OF FINAL SEDIMENTATION TANKS:
VARIATION OF THE ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS:
- Activated sludge was introduced in 1941 and has undergone many variations and adaptations.
- The main objective of many modifications has been to increase the loading capacity of the basic plug flow activated sludge plant by provision of optimum condition design parameters for different variations are summarized in table. It is worthy of note that 5 modifications tapered aeration step aeration the CMAS process, the pure oxygen system and the deep shaft process all aim at either the improvement of oxygen transfer efficiency t the efficient distribution of available oxygen to match demand. A flow sheet of most of the commonly used variations is similar to that of CAS (Conventional Activated Sludge).
CONVENTIONAL ACTIVATED SLUDGE:
Volumetric loading = kg of BOD
m3-d
Aerial loading rate = gm of BOD
m3-d
Td = V/Q in days and grater than 5 days.
ALGAL-BACTERIAL SYMBOPSTS:
The combined and mutually- been facial action of algae and bacteria in this process is called algal-bacterial symbioses.
- Shock loading (CSTR)
- BODu
Aerated Lagoons:
Aerate lagoons are activated sludge units operated without sludge return. Historically they were developed from waste stabilization ponds in temperate climate where mechanical aeration was used to supplement the algal oxygen supply in winter. It was found, however that soon after the aerations were put into operation the algal disappeared and the microbial flora resembled that of activated sludge. Aerated lagoons were now usually design as completely mixed not-return activated sludge units. Floating aerates are most commonly used to supply the necessary oxygen and mixing power.
Sludge Treatment:
Anaerobic sludge treatment cell Primary Sedimentation Tank and Secondary Sedimentation Tank are basically organic these can treated to aerobic.
- Anaerobic ponds and septic tank are for waste water treatment .
- Sludge treatment = Anaerobic sludge treatment.
COLD DIGESTION:
- Two stage digestion up
- High rate digestion up
- Fixed film processes. A swm zone
SLUDGE DIGESTION:
SLUDGE: the concentrated impurities settled at the bottom of the flower bed of sedimentation tanks.
Digestion:
To decompose or breakdown by heat and moisture or chemical action. (to invent food equable forms)
Sludge treatment:
Aerobic digestion it is defined as ‘it is the use of microbial organisms in the absence of oxygen I for the stabilization of oxygen materials by conversion to mean and inure produce including CO2.
Organic matter + H2O (amoebas) CH4+ CO2 + NH3+ H2S + heat
Benefices of anaerobic digestion. Types of anabolic detectors. It’s of two types:
- Conventional (stranded) or low-rate digester or cold digester.
- High rate digesters / two stage digester are characterized by continuous miring except at time of sludge with draw.