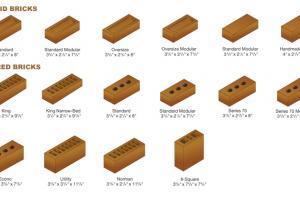
Types of Bricks and Classification of Bricks based on different Factors
Definition
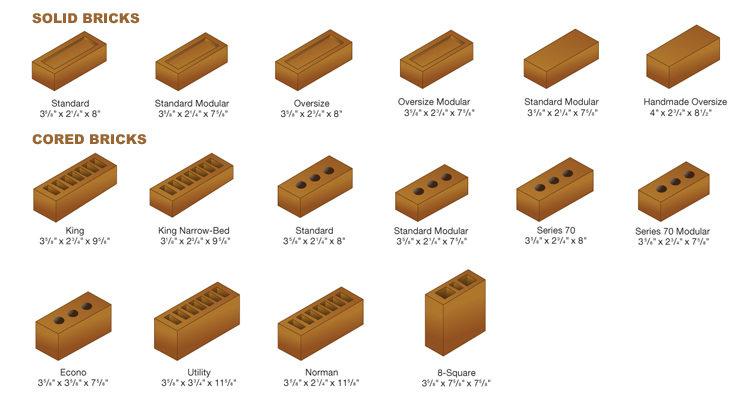
Brick is the smallest building unit made up of Silica, Clay, Lime, Iron Oxide, and Magnesia. There are many types of bricks in the construction industry that are defined on the basis of different criteria. Typical bricks are 9" long, 4.5" wide, and 3" thick. Bricks are widely used in masonry construction due to their aesthetic value, high compressive strength, and fire protection and provide the required wear resistance.
Types of Bricks
Classification of Bricks
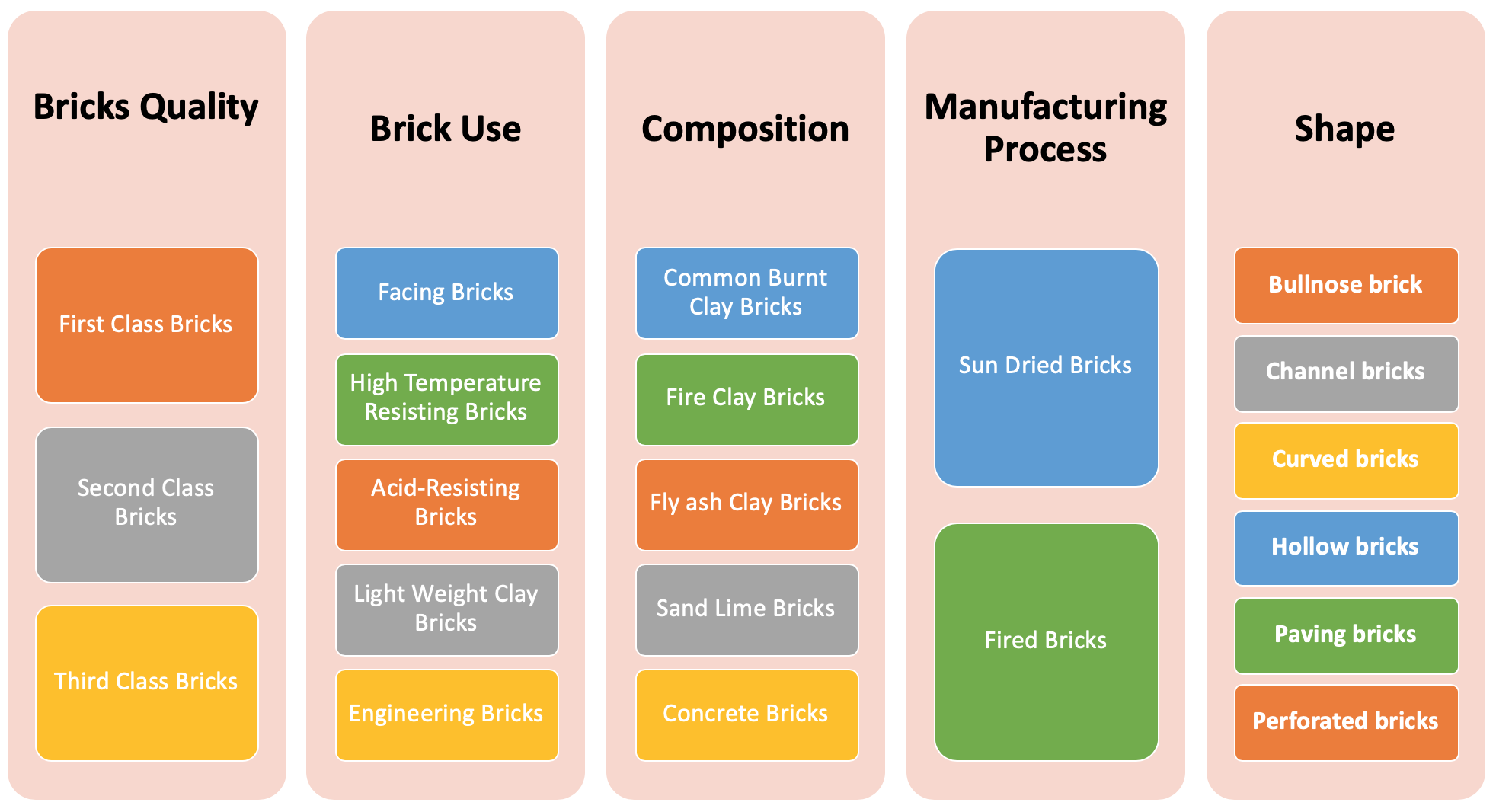
Bricks in masonry construction can be classified on the basis of the following criteria:
- Quality of Bricks
- Uses and Applications of Bricks
- Composition of Bricks
- The Manufacturing Process of Bricks
1. Classification of Bricks Based on Quality
First-Class Bricks:
First-class bricks are considered the highest quality bricks available. These bricks are well-shaped, sharp-edged, and have uniform color and texture. They are made from high-grade clay or shale, which is thoroughly mixed and molded under controlled conditions. First-class bricks undergo a strict quality control process during manufacturing to ensure their strength and durability. They have a uniform water absorption rate of about 20%, making them ideal for load-bearing structures.
Second-Class Bricks:
Second-class bricks are of slightly lower quality compared to first-class bricks. They may have slight irregularities in shape, size, and color. Although they may not be as aesthetically pleasing as first-class bricks, they still possess good strength and durability. Second-class bricks are often used in non-load-bearing walls, plastering works, and other areas where their appearance is not a primary concern. These bricks have a water absorption rate of around 22% to 25%.
Third-Class Bricks:
Third-class bricks are the lowest-quality bricks available. They have a rough and uneven surface, irregular shape, and may contain small cracks or distortions. These bricks are made from inferior clay or shale and are often overburnt during the firing process. Third-class bricks have a high water absorption rate of around 25% to 30% and are not suitable for load-bearing structures. They are commonly used in temporary structures, garden walls, and areas where their strength requirements are minimal.
Overburnt Bricks:
Over-burnt bricks are a subcategory of third-class bricks. These bricks are the result of excessive heat during the firing process, causing them to become dark in color, brittle, and less dense. Over burnt bricks have poor structural integrity and are highly porous, absorbing water up to 35%. Due to their low strength and high water absorption, they are not recommended for use in construction.
Underburnt Bricks:
Under-burnt bricks are another subcategory of third-class bricks. These bricks are not adequately fired, resulting in a pale or light-colored appearance. Under burnt bricks are weak and have low durability, making them unsuitable for structural applications. They have a high water absorption rate, typically above 30%. Due to their low strength and poor quality, underburnt bricks are generally avoided in construction projects.
2. Types of Bricks Based on Uses
Common Bricks:
Common bricks are the most widely used type of bricks in construction. They are generally made from clay and have a rectangular shape with standard dimensions. These bricks are suitable for general purposes and can be used in both load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls. Common bricks offer good strength and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of construction projects.
Facing Bricks:
Facing bricks, also known as face bricks or facade bricks, are primarily used for their aesthetic appeal. These bricks are carefully manufactured to have an attractive and uniform appearance. They come in different colors, textures, and patterns, allowing builders and architects to create visually appealing exteriors for buildings. Facing bricks are often made from high-quality clay and undergo additional processes to enhance their visual appeal and durability.
Fire Bricks:
Fire bricks, also called refractory bricks, are designed to withstand high temperatures. They are made from special clay or other refractory materials, such as alumina, silica, or magnesia. Fire bricks are used in applications where heat resistance is essential, such as fireplaces, kilns, furnaces, and industrial chimneys. These bricks have excellent thermal insulation properties, making them capable of withstanding extreme temperatures without significant structural damage.
Engineering Bricks:
Engineering bricks are a robust and durable type of bricks used in heavy-duty construction. They are manufactured using high-density clay and are designed to withstand high loads and adverse weather conditions. Engineering bricks have high compressive strength and low water absorption, making them suitable for applications where strength and resistance to moisture are crucial. They are commonly used in retaining walls, basements, and areas prone to chemical exposure.
Perforated Bricks:
Perforated bricks, as the name suggests, have small holes or perforations through their structure. These holes help in improving the brick's thermal insulation properties, as well as reducing its weight. Perforated bricks are commonly used in areas where insulation is required, such as cavity walls or buildings located in extreme climate conditions. The holes also provide better bonding when used with mortar, enhancing the overall structural integrity.
Hollow Bricks:
Hollow bricks are lightweight and have hollow cavities within their structure. These cavities significantly reduce the weight of the brick while maintaining its strength. Hollow bricks offer excellent thermal insulation properties and are commonly used in the construction of partition walls, infill walls, and non-load-bearing structures. They also provide better sound insulation and are easy to handle and transport due to their reduced weight.
Concrete Bricks:
Concrete bricks are made from a mixture of cement, aggregates, and water. They are widely used in construction due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Concrete bricks can be solid or hollow, and their composition can be varied to achieve specific strength requirements. These bricks are commonly used in load-bearing walls, retaining walls, and other structural applications.
Special Purpose Bricks:
Apart from the above-mentioned types, there are various special-purpose bricks designed for specific applications. These include acid-resistant bricks for chemical industries, soundproof bricks for noise reduction, water-resistant bricks for damp areas, and thermal-insulating bricks for energy-efficient construction. Special-purpose bricks cater to unique requirements and play a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and functionality of specific structures.
3. Types of Bricks Based on its Composition
There are various types of bricks used in masonry:
Clay Bricks:
Clay bricks are the most common type of bricks and have been used for thousands of years. They are made from natural clay, which is molded and then fired in a kiln. Clay bricks offer excellent strength, durability, and thermal insulation properties. They are suitable for both load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls and are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects.
Concrete Bricks:
Concrete bricks are manufactured by mixing cement, sand, aggregate, and water. The mixture is then poured into molds and cured to form solid bricks. Concrete bricks offer high compressive strength and durability. They are commonly used in load-bearing walls, retaining walls, and other structural applications. Concrete bricks can also be made with hollow cores to reduce weight and improve insulation.
Fly Ash Bricks:
Fly ash bricks are an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional clay bricks. They are made from a combination of fly ash (a byproduct of coal combustion), sand, and cement. Fly ash bricks are lightweight, durable, and possess good thermal insulation properties. They are commonly used in construction projects where sustainability and energy efficiency are prioritized.
Sand-Lime Bricks:
Sand-lime bricks are made from a mixture of sand, lime, and water. The mixture is molded under high pressure and then cured in an autoclave or steam chamber. Sand-lime bricks offer high strength, good fire resistance, and excellent sound insulation properties. They are commonly used in load-bearing walls, flooring, and areas where fire safety is crucial.
Fire Bricks:
Fire bricks, also known as refractory bricks, are designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. They are made from special refractory materials, such as clay, alumina, silica, or magnesia. Fire bricks are commonly used in applications where heat resistance is essential, such as fireplaces, kilns, furnaces, and industrial chimneys. They have excellent thermal insulation properties and can withstand extreme temperatures without significant structural damage.
Calcium Silicate Bricks:
Calcium silicate bricks, also known as sand-lime bricks, are made from sand, lime, and water. They are formed by pressing the mixture into molds and then autoclaved to enhance their strength and durability. Calcium silicate bricks offer good load-bearing capacity, low thermal conductivity, and resistance to fire and moisture. They are commonly used in construction projects that require high-quality bricks with superior insulation and durability.
Magnesia Bricks:
Magnesia bricks are made from magnesium oxide (magnesia) and other refractory materials. They possess excellent high-temperature resistance and are commonly used in applications such as steel-making furnaces, cement kilns, and other industrial processes that require resistance to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Porotherm Bricks:
Porotherm bricks are a type of clay brick with vertical perforations. These perforations not only reduce the weight of the brick but also enhance its thermal insulation properties. Porotherm bricks offer good compressive strength and are commonly used in residential and commercial construction, especially in areas with extreme weather conditions.
4. Based on Manufacturing Process
- Sun Dried Bricks
- Fired Bricks
- Solid
- Hollow
- Perforated
- Cellular
- Concrete
- Sand-Lime
- Fly-Ash
- Concrete Blocks
Unburnt/ Sun-Dried Bricks:
Unburnt or sun-dried bricks are one of the oldest forms of bricks, traditionally made by shaping clay and allowing it to dry naturally under the sun. These bricks are not fired in a kiln. Sun-dried bricks are typically used for temporary structures, non-load bearing walls, and in rural areas where the availability of fuel for firing is limited. While they are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, sun-dried bricks have limited strength and durability.
Burnt/ Fired Bricks:
Fired bricks are the most commonly used type of bricks in construction. They are manufactured by subjecting molded clay to high temperatures in a kiln, resulting in a chemical and physical transformation of the clay. There are several subtypes of fired bricks, including:
Solid Bricks:
Solid bricks are compact, dense bricks that are uniformly fired. They are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for load-bearing structures.
Hollow Bricks:
Hollow bricks have hollow cavities within their structure, which reduce their weight and improve their thermal insulation properties. These bricks are commonly used in non-load bearing walls.
Perforated Bricks:
Perforated bricks have regular holes or perforations running through them, resulting in reduced weight and enhanced thermal insulation. They are often used in partition walls or where a reduction in overall weight is desired.
Cellular Bricks:
Cellular bricks have a cellular or honeycomb-like structure, which provides excellent thermal insulation. They are lightweight and offer good load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for both load-bearing and non-load bearing applications.
Concrete Bricks:
Concrete bricks are made by combining cement, aggregates, and water, which are then molded and cured. These bricks are often larger in size compared to traditional clay bricks and offer high strength and durability. Concrete bricks can be manufactured in various shapes, sizes, and textures, allowing for a wide range of design possibilities in construction projects.
Sand-Lime Bricks:
Sand-lime bricks are manufactured by mixing sand, lime, and water, followed by compaction and steam curing. The combination of sand and lime provides excellent strength and durability to these bricks. Sand-lime bricks have uniform shapes and sizes, high compressive strength, and good resistance to moisture, making them suitable for load-bearing structures.
Fly Ash Bricks:
Fly ash bricks are manufactured using fly ash, a byproduct of coal combustion, combined with cement, sand, and water. These bricks are environmentally friendly, as they make use of a waste material and require less energy during the manufacturing process. Fly ash bricks offer good strength, thermal insulation, and fire resistance.
Concrete Blocks:
Concrete blocks, also known as concrete masonry units (CMUs), are large rectangular bricks made from a mixture of cement, aggregates, and water. These blocks are primarily used for load-bearing walls and offer high strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy. Concrete blocks come in various sizes, shapes, and configurations to meet specific construction requirements.