Design & Construction of Culverts

Culvert Definition
A culvert is a structure (transverse and totally enclosed drain) that allows water to flow underneath a roadway, railroad, embankment, or another type of transportation infrastructure. It is typically a pipe or a box-like structure made of concrete, steel, or other materials, and it is designed to channel water away from the roadway or different structures it crosses.
OR
A watercourse totally enclosed and usually of a size through which a man can pass
OR
An opening through an embankment for the conveyance of water by means of a pipe or an enclosed channel.
Some considerations for use of Culvert
Culverts are used to prevent flooding and erosion by allowing water to pass under transportation infrastructure without causing damage to the roadway or embankment. They can also be used to redirect water from one area to another, such as in drainage systems.
- For small openings, pipes in stock size are employed, with pipe arch as a substitute where headroom is limited.
- For larger openings, single or multiple-span box culverts are generally used. However, one or more large-diameter pipes of RCC are preferred.
- Bridge culverts replace box culverts where the foundation is non-erodible and a paved floor is not necessary.
- Generally, the selection and type of material depend on the comparative cost, location of the structure, availability of skilled labor, and time limitations.
- Culvert begins upstream with headwalls and terminates downstream with end walls.
- Headwalls direct flow into a culvert, properly while end walls provide a transition from the culvert bank to the regular channel. Both protect the embankment from washing away by flood waters.
Types of Culverts
Culverts come in various sizes and shapes depending on the amount of water they need to accommodate, the width of the roadway they are crossing, and the type of material used in their construction. Some culverts may be reinforced with steel or other materials to make them stronger, while others may be lined with concrete or other materials to prevent erosion.
|
Type of culvert
|
Typical Cross Section of culverts
|
Common Material used for culverts
|
|
Pipe Single or Multiple |
 |
Corrugated Material, Plain or Reinforced Concrete, Vitrified Clay, Cast Iron. |
| Pipe Arch Single or Multiple |
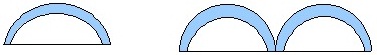 |
Corrugated Material |
| Box Culvert Single or Multiple |
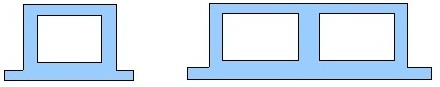 |
Reinforced Concrete |
|
|
||
| Bridge Culvert |
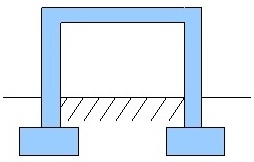 |
Reinforced Concrete |
|
Arch |
 |
RCC, Corrugated Metal, Stone Masonry Arch |