What is BRT Peshawar and its Project Details
BRT
BRT stands for Bus Rapid Transit. Bus rapid transit (BRT, BRTS, busway, transitway) is a bus-based public transport system designed to improve capacity and reliability relative to a conventional bus system.
BRT Corridor
A BRT corridor is section of road or contiguous roads served by a bus route or multiple bus routes with a minimum length of 3 kilometers (1.9 miles) that has dedicated bus lanes.
Peshawar BRT
The project is named as "Peshawar Sustainable Bus Rapid Transit Corridor Project".
Location
The Project alignment starts from Chamkani on GT Road through Pir Zakori Bridge, Peshawar Bus Terminal, Hashtnagri, Hospital Road, Khyber Bazar, Soekarno Chowk, Shoba Chowk, Railway Road, Sunehri Masjid Road, Aman Chowk, University Road, Board Bazar, Jamrud Road and terminates at Hayatabad Phase-V.
Planning and Execution
A 20 year public transport road map was developed in Urban Transport Pre-feasibility Study (PFS) which was completed under City Development Initiative for Asia (CDIA) in May, 2014. Six corridors were identified by the Pre-feasibility Study which formed the basis for Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system of Peshawar. They are to be developed through a phased, corridor-based investment program as part of the 20-year public transport road-map.
The project is being undertaken by the GoKP as a high priority project conceived by CDIA pre-feasibility study (May, 2014) and PPTA feasibility/ preliminary engineering design study (Dec, 2016). Both studies were undertaken through ADB grant.
Planning and Development Department Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Annual Development Program) with Financial Assistance from Asian Development Bank (ADB) are the main sponsors of this project whereas, TransPeshawar and Peshawar Development Authority (PDA) under the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Urban Mobility Authority (KPUMA) is executing the project. The maintenance and operations of the BRT Peshawar will also be carried out by KPUMA and TransPeshawar.
Objectives of Peshawar BRT
Available transportation facilities are highly deficient and of inferior quality. Old model Buses, Mazda/Mini Buses, Suzuki Pickups, Datsun Pickups and Ford wagons of various sizes are the only option for the commuters traveling through public transport facilities. The existing transportation system is thus facing multiple problems such as over-population, lack of planning & regulation, absence of public transport infrastructure, poor design and management of road infrastructure, no traffic management and reliance on private vehicles which are ultimately causing dire traffic congestion in peak hours and severe environmental issues. Therefore, there is a need to address these problems in a holistic manner following the principles of sustainable transportation planning and management.
The project is aimed to achieve the following objectives:
- To introduce well planned, designed, efficient, reliable, and comfortable user friendly Bus Rapid Transit system which will be integrated with existing transport facilities
- To provide infrastructure that allows buses to ply in an efficient manner with dedicated right of way for a significant portion of route length
- To introduce feeder routes along with main BRT corridor to accommodate major high capacity existing radial routes
- Provision of Park & Ride facilities with an integration to major commercial centers to minimize private vehicle dependence
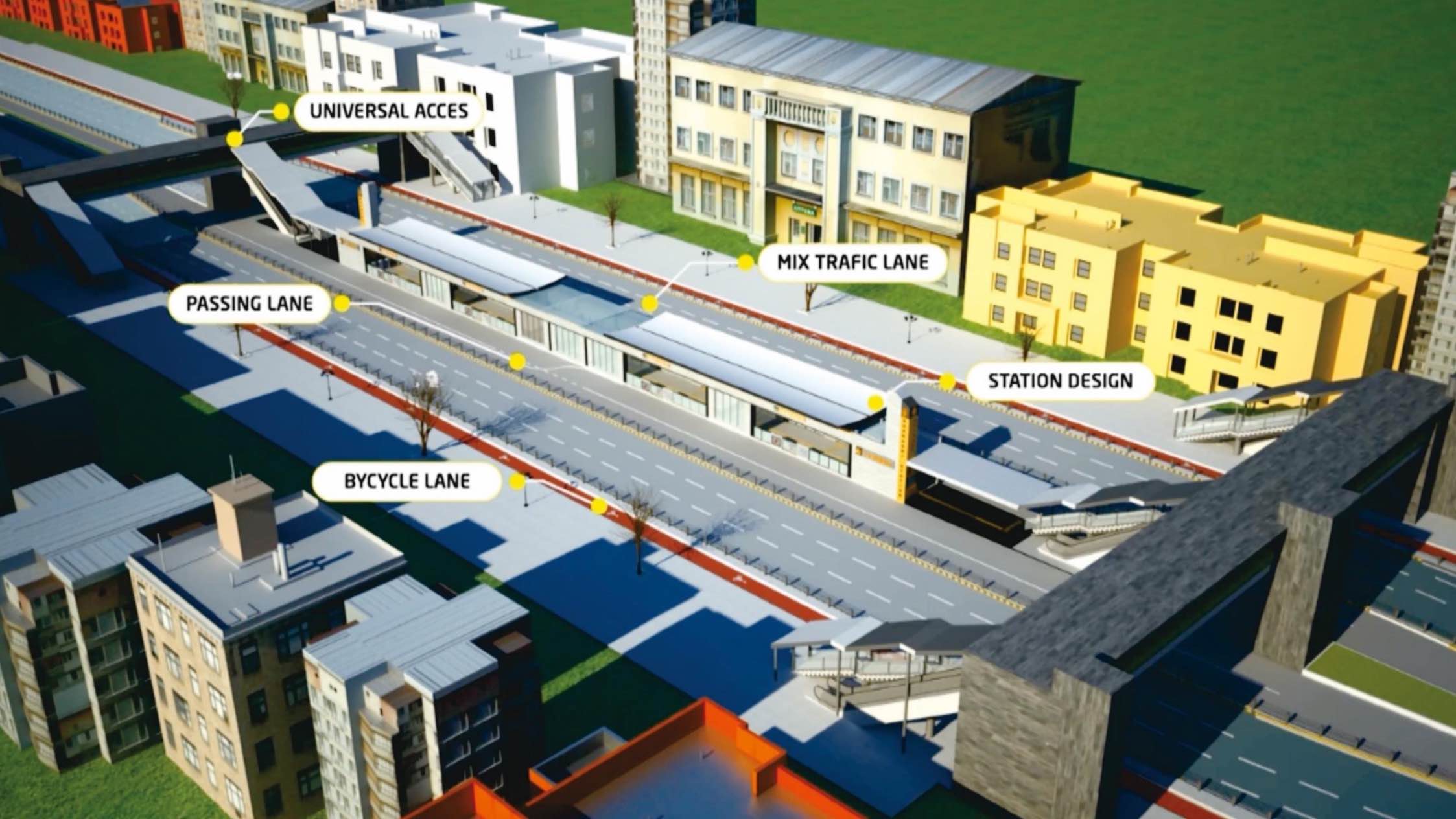
- Provision of Walking and Cycling facilities and it’s integration with BRT system to make city more accessible for Non-Motorized Travel
- To overall reduce travel time and delays for whole transport system of Peshawar
- To improve the quality of life of commuters in Peshawar
- Provide safe, efficient, and well-integrated mass transit system with focus on reliability, affordability, and convenience
- Improve safety, energy efficiency and air quality through minimizing private vehicle use
- Strengthen existing transportation infrastructure and services by adopting various alternatives
- Develop transport infrastructure to support and intensify existing land-use through the introduction of Transit Oriented Development (TOD), leading to densification and enhancement of commercial activities.
- A mass transit System (MTS) that facilitates and encourages high density commercial and residential development, and leads to containment of urban sprawl
- Minimize duplication / overlapping of public transport on formal & informal routes
- Maximize ridership and ensures integration with other transport modes, and is in line with land use and caters to activity centers i.e. Transport Oriented Development
- High level of service in terms of speed, safety, frequency and accessibility (geographical and financial), which reduces dependence on other forms of transport (cars, rickshaws and motorcycles etc.)
- Safe, secure, reliable, comfortable, and environmentally sustainable transport system; which meets the needs and aspirations of people of Peshawar.
Project Description
Peshawar BRT system will have many the following additional features:
- 68 Km Feeder bus route service excluding main BRT Corridor Overlap (7 routes),
- 150 standard Bus Stops at feeder routes
- 450 Buses of 9m and 12m and 18m BRT buses
- 61 Kanal of Commercial Area Development,
- 6 Stories Parking Plaza at Lady Reading Hospital provided with 15 electric vehicles for patient transfer,
- Bike Sharing Scheme at University of Peshawar vii. Segregated cycle lane along the length of BRT Corridor
- Pedestrian Infrastructure improvement and networking along the BRT Corridor.
- Shops at selected over-bridges and BRT Stations.
- Provision of Rest Rooms/Lavatories at all BRT Stations and at various locations along the BRT Corridor.
In addition to the above features, Main BRT Corridor include innovative stations design equipped with public facilities like parking for bicycles, and water filtration plant. Moreover, Non-Motorized Transport (NMT) is promoted to create a healthy livable environment, for which, sidewalk provisions, pedestrian crossing bridges, and pedestrian only tunnels with commercial shops are provided at different locations.
Peshawar BRT Corridor
The proposed BRT corridor of 25.8km is designed as a signal free corridor, which starts from Chamkani on GT Road through Pir Zakori Bridge, Peshawar Bus Terminal, Hashtnagri, Hospital Road, Khyber Bazar, Soekarno Chowk, Shoba Chowk, Railway Road, Sunehri Masjid Road, Aman Chowk, University Road, Jamrud Road and terminates at Hayatabad Phase-V. The corridor will be mostly at-grade, whereas elevated U-turns and BRT only elevated segments & tunnels are provided at certain locations to remove the conflict with mix traffic.
Peshawar Mass Transit Routes
The project includes construction of dedicated BRT with seven BRT feeder routes integrated with main corridor covering major trip generation areas of the city: Charsada Road, Warsak Road, Kohat Road, Bara Road, Ring Road, and Jamrud Road.
Cost of Peshawar Metro
Cost: Rs 57.86 billion is for;
- BRT Infrastructure construction
- ITS and fare collection
- Bus depots and staging facility construction
- Bike Share System
- Parking Plazas with Commercial Development
- Buses procurement
- Institutional Development
- Utilities & Resettlement Cost
The project is consistent with the Government of Pakistan''s Vision 2025, Framework for Economic Growth (2011), National Climate Change Policy; supports priorities set out in KPK Comprehensive Development Strategy 2010-17; and is aligned with the interim country partnership and Sustainable Transport Initiative of the Asian Development Bank. It will contribute to make Peshawar safer and more business-friendly through low carbon and climate resilient urban infrastructure and improved access. The project design will incorporate lessons learned from past assistance, notably the need for strong political support and consensus, and for a robust governance structure. Coordination will be ensured with development partners and potential co-financiers in the urban transport sector.