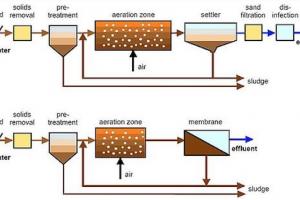
Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment Process

- Unit process
- Biological treatment process
- Suspended growth process
- Aerobic process
Activated Sludge:
Definition
Is defined as a ‘Suspension’ of microorganisms, both living and dead’ in a wastewater. The microorganisms are active by an input of air (oxygen) thus known as activated-sludge. Activate-sludge is that sludge which settle down in a secondary sedimentation tank after the sewage has been freely aerated and agitated for a certain time in an Aeration tank.
Working Mechanism of Activated Sludge
The activated-sludge contains numerous bacteria and other microorganisms, when it is mixed with raw sewage saturated with oxygen, the bacteria perform the following function.
- Oxidize the organic solids.
- Promote coagulation and flocculation and convert dissolved, colloid and suspended solids into settle able solids. In practice the following operations are carried out in an activated - sludge process.
- The sewage is given treatment in the primary sedimentation tank. The detention time is kept as short as 1-1/2 hours.
- The settled sewage form the Primary Sedimentation Tank is the mixed with the required quantity of activated-sludge in the aeration tank. The mixture of activated-sludge and wastewater in the aeration tank is called ‘mixed liquor or mixed liquor suspended solids MLSS or MLVSS mixed liquor volatile suspended solids’.
- The Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids is aerated for 6-8 hours in the aeration tank, called the hydraulic detention time according to the degree of purification. About 8m3 of air is provided from each m3 of waste-water treated. The volumes of sludge returned to the aeration basin is typically 20 to 30% of waste water flow air supply 8-10 m3 of sewage
- The aerated Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids resulting in the formation of flock particles, ranging in size from 50 to 200pm.which is then removed in the secondary sedimentation tank by gravity settling, leeching a relatively clear liquid as the treated effluent. Typically greater than 99% of suspend solids can be removed in the clarification step.
- Most of the settled sludge is returned to the aeration tank (and is called return sludge) to maintain the high population of microbes that permits rapid breakdown of the organic compounds. Because more activated-sludge is produced tan is desirable in the process, some of the return sludge is diverted or wasted to the sludge handling system for treatment and disposal.
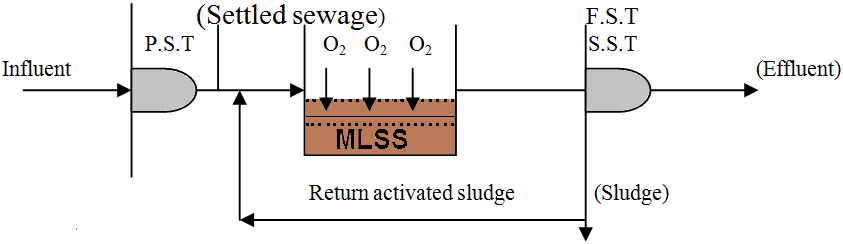
Activated Sludge Process
Consists of three basic components:
- Reactor in which microorganisms responsible for treatment are kept in suspension and aerated;
- Liquid-solids separation usually in sedimentation tank;
- Recycle system for returning solids removed from liquid-solids separation unit back to reactor;
Important feature is formation of flocculent settleable solids removed by gravity settling in sedimentation tanks. Pretreatment with primary sedimentation removes settleable solids whereas biological processes remove soluble, colloidal, and particulate (suspended) organic substances; for biological nitrification and denitrification; and for biological phosphorus removal.